Figure 78
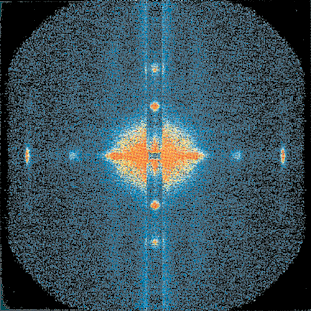 a)
a)
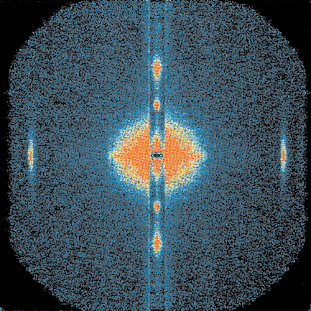 b)
b)
Fig. 78: Diffraction patterns from an isolated muscle fibre a) in the resting state and b) at the plateau of isometric contraction. Each pattern is the result of a total 10 s exposure. The horizontal axis is called the meridian and corresponds to the fibre axis. The vertical axis is called the equator. The layer line at 42.9 nm arises from the helical arrangement of cross-bridges on the myosin filament, and the strong meridional reflection on third layer line (14.3 nm) arises from the axial repeat of myosin heads. The equatorial reflections are due to the hexagonal array of the filaments in the cross-section of the fibre: (1,0), spacing 37 nm and (1,1), spacing 21 nm.



